
SL Paper 1
Which changes could take place at the positive electrode (cathode) in a voltaic cell?
I. \({\text{Z}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}}\) to Zn(s)
II. \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}}\) to \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}}\)
III. Mg(s) to \({\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}}\)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
What occurs at the anode (positive electrode) during the electrolysis of molten strontium bromide?
A. Formation of bromine and oxidation
B. Formation of bromine and reduction
C. Formation of strontium and oxidation
D. Formation of strontium and reduction
What happens to the manganese in the following reaction?
\[{\text{2MnO}}_4^ - {\text{(aq)}} + {\text{5}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{6}}{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} \to {\text{2M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{8}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(l)}} + {\text{5}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}}\]
A. It is oxidized and its oxidation number increases.
B. It is oxidized and its oxidation number decreases.
C. It is reduced and its oxidation number increases.
D. It is reduced and its oxidation number decreases.
What is the order of decreasing reactivity of the metals (most reactive first)?
Zn(s) + Sn2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Sn(s)
Cu(s) + Zn2+(aq) → No Reaction
Sn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Sn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
Ag(s) + Cu2+(aq) → No Reaction
A. Zn > Cu > Sn > Ag
B. Sn > Zn > Ag > Cu
C. Ag > Cu > Zn > Sn
D. Zn > Sn > Cu > Ag
What is the oxidation half-equation in the redox reaction?
2S2O32–(aq) + I2(aq) → S4O62–(aq) + 2I–(aq)
A. I2(aq) + 2e– → 2I–(aq)
B. 2I–(aq) → I2(aq) + 2e–
C. 2S2O32–(aq) → S4O62–(aq) + 2e–
D. S4O62–(aq) + 2e– → 2S2O32–(aq)
What occurs during the operation of a voltaic cell based on the following overall reaction?
\[2{\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{Cu(s)}} \to {\text{2Ag(s)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{u}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}}\]

What is the name of \({\text{C}}{{\text{u}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}\)?
A. Copper(I) sulfide
B. Copper(I) sulfate
C. Copper(II) sulfide
D. Copper(II) sulfate
What is the correct decreasing order of reactivity of the metals X, Y and Z based on the following equations?
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{\text{XCl}} + {\text{Y}} \to {\text{YCl}} + {\text{X}}} \\ {{\text{YCl}} + {\text{Z}} \to {\text{YCl}} + {\text{Z}}} \\ {{\text{ZCl}} + {\text{X}} \to {\text{XCl}} + {\text{Z}}} \end{array}\]
A. X \( > \) Y \( > \) Z
B. Y \( > \) Z \( > \) X
C. Z \( > \) Y \( > \) X
D. Y \( > \) X \( > \) Z
Which can describe oxidation?
A. Loss of hydrogen
B. Decrease in oxidation number
C. Gain of electrons
D. Loss of oxygen
Which element is reduced in the following decomposition?
(NH4)2Cr2O7(s) → N2(g) + Cr2O3(s) + 4H2O(g)
A. N
B. H
C. Cr
D. O
What is produced at the positive electrode (anode) and negative electrode (cathode) during the electrolysis of molten lithium chloride and molten lead bromide?

Which of the following is not a redox reaction?
A. CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g)
B. C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
C. 2CO(g) → CO2(g) + C(s)
D. CH3COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) → CH3COONa(aq) + H2O(l)
Which of the following is a redox reaction?
A. 3Mg (s) + 2AlCl3 (aq) → 2Al (s) + 3MgCl2 (aq)
B. SiO2 (s) + 2NaOH (aq) → Na2SiO3 (aq) + H2O (l)
C. KCl (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) → AgCl (s) + KNO3 (aq)
D. 2NaHCO3 (aq) → Na2CO3 (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
Consider the following reaction:
\[3{\text{S}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}({\text{aq)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }{\text{(aq)}} + 2{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} \to 2{\text{C}}{{\text{r}}^{3 + }}{\text{(aq)}} + 3{\text{Sn}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(s)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}}\]
Which statement is correct?
A. \({\text{S}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}\) is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation.
B. \({\text{S}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}\) is the reducing agent because it undergoes oxidation.
C. \({\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }\) is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation.
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }\) is the reducing agent because it undergoes oxidation.
What happens at the negative electrode in a voltaic cell and in an electrolytic cell?

Which statement is correct for a voltaic but not for an electrolytic cell?
A. An electrolyte is required.
B. The anode is where oxidation occurs.
C. Ions move in the electrolyte.
D. Electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode.
Consider the following reactions of three unknown metals X, Y and Z.
\({\rm{2XN}}{{\rm{O}}_3}{\rm{(aq)}} + {\rm{Y(s)}} \to 2{\rm{X(s)}} + {\rm{Y(N}}{{\rm{O}}_3}{)_2}{\rm{(aq)}}\)
\({\rm{Y(N}}{{\rm{O}}_3}{)_2}{\rm{(aq)}} + {\rm{Z(s)}} \to\) No reaction
\(2{\rm{XN}}{{\rm{O}}_3}{\rm{(aq)}} + {\rm{Z(s)}} \to 2{\rm{X(s)}} + {\rm{Z(N}}{{\rm{O}}_3}{)_2}{\rm{(aq)}}\)
What is the order of increasing reactivity of the metals (least reactive first)?
A. \({\text{X}} < {\text{Y}} < {\text{Z}}\)
B. \({\text{X}} < {\text{Z}} < {\text{Y}}\)
C. \({\text{Z}} < {\text{Y}} < {\text{X}}\)
D. \({\text{Y}} < {\text{Z}} < {\text{X}}\)
Which is a correct statement for the reaction below?
2MnO4-(aq) + 6H+(aq) + 5NO2-(aq) → 2Mn2+(aq) + 5NO3-(aq) + 3H2O(l)
A. MnO4- is the reducing agent and the oxidation number of Mn increases.
B. MnO4- is the oxidizing agent and the oxidation number of Mn decreases.
C. NO2- is the reducing agent and the oxidation number of N decreases.
D. NO2- is the oxidizing agent and the oxidation number of N increases.
Which element has the same oxidation number in both species?
A. C in C2H4 and CO2
B. H in H2O and NaH
C. S in SO42−and SO3
D. O in H2O2 and H2O
Consider how current is conducted in an electrolytic cell. Which statement is correct?
A. Electrons move through the electrolyte and the external circuit.
B. Ions move through the electrolyte and the external circuit.
C. Electrons move through the external circuit and ions move through the electrolyte.
D. Electrons move through the electrolyte and ions move through the external circuit.
Which experimental methods could be used to observe the progress of the following reaction?
Cr2O72-(aq) + 6I-(aq) + 14H+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3I2(aq) + 7H2O(l)
I. Change in colour
II. Change in mass
III. Change in electrical conductivity
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Metal A is more reactive than metal B. A standard voltaic cell is made as shown.

Which statement is correct?
A. Electrons flow in the external circuit from A to B.
B. Positive ions flow through the salt bridge from A to B.
C. Positive ions flow in the external circuit from B to A.
D. Electrons flow through the salt bridge from B to A.
Applying IUPAC rules, what is the name of MnO2?
A. Magnesium(II) oxide
B. Manganese(II) oxide
C. Magnesium(IV) oxide
D. Manganese(IV) oxide
Which statements are correct for a voltaic cell?
\(\begin{gathered} \begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{\text{I.}}}&{{\text{A spontaneous redox chemical reaction produces electrical energy.}}} \\ {{\text{II.}}}&{{\text{Oxidation occurs at the cathode (negative electrode).}}} \\ {{\text{III.}}}&{{\text{Electrons flow from anode (negative electrode) to cathode (positive electrode).}}} \end{array} \hfill \\ \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which of the following redox reactions take place?
I. \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{2NaI(aq)}} \to {{\text{I}}_2}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{2NaCl(aq)}}\)
II. \({\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{2NaI(aq)}} \to {{\text{I}}_2}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{2NaBr(aq)}}\)
III. \({{\text{I}}_2}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{2NaBr(aq)}} \to {\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{2NaI(aq)}}\)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Metal M has only one oxidation number and forms a compound with the formula \({\text{MC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\). Which formula is correct?
A. \({\text{MN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({\text{MN}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\)
C. \({\text{MS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\)
D. \({\text{MP}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\)
Which are redox reactions?
I. \({\text{2FeC}}{{\text{l}}_2} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2} \to 2{\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\)
II. \({\text{Mg}} + {\text{2HN}}{{\text{O}}_3} \to {\text{Mg(N}}{{\text{O}}_3}{)_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}\)
III. \({{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_3} \to {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}\)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
What is the correct increasing order of reactivity of the metals X, Y and Z based on the following information?
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{\text{XC}}{{\text{l}}_2} + {\text{Y}} \to {\text{YC}}{{\text{l}}_2}{\text{X}}} \\ {{\text{ZC}}{{\text{l}}_2} + {\text{X}} \to {\text{XC}}{{\text{l}}_2}{\text{Z}}} \\ {{\text{YC}}{{\text{l}}_2} + {\text{Z}} \to {\text{no reaction}}} \end{array}\]
A. \({\text{Z}} < {\text{X}} < {\text{Y}}\)
B. \({\text{Y}} < {\text{X}} < {\text{Z}}\)
C. \({\text{Z}} < {\text{Y}} < {\text{X}}\)
D. \({\text{X}} < {\text{Z}} < {\text{Y}}\)
Which statement is correct for the following reaction?
\[{\text{2ClO}}_3^ - {\text{(aq)}} + {\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} \to {\text{2Cl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{HSO}}_4^ - {\text{(aq)}}\]
A. \({\text{ClO}}_3^ - \) is the oxidizing agent and it undergoes reduction.
B. \({\text{ClO}}_3^ - \) is the reducing agent and it undergoes oxidation.
C. \({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) is the oxidizing agent and it undergoes oxidation.
D. \({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) is the reducing agent and it undergoes reduction.
What are the products of electrolysis when molten calcium bromide is electrolysed using graphite electrodes?

Which statement describes a reducing agent?
A. It is reduced and gains electrons.
B. It is reduced and loses electrons.
C. It is oxidized and gains electrons.
D. It is oxidized and loses electrons.
What is the reducing agent in the reaction below?
\[2{\text{MnO}}_4^ - ({\text{aq)}} + {\text{B}}{{\text{r}}^ - }({\text{aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} \to {\text{2Mn}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(s)}} + {\text{BrO}}_3^ - ({\text{aq)}} + 2{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }({\text{aq)}}\]
A. \({\text{B}}{{\text{r}}^ - }\)
B. \({\text{BrO}}_3^ - \)
C. \({\text{MnO}}_4^ - \)
D. \({\text{Mn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\)
At which side of the equation are electrons, \({{\text{H}}^ + }\) ions and \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\) needed to complete the half-equation?
\[{\text{MnO}}_4^ - {\text{(aq)}} \to {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}}\]

Which species could be reduced to form \({\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\)?
A. \({{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\)
B. \({\text{NO}}_3^ - \)
C. \({\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. NO
Zinc is more reactive than copper. In this voltaic cell, which species is reduced and in which direction do negative ions flow in the salt bridge?
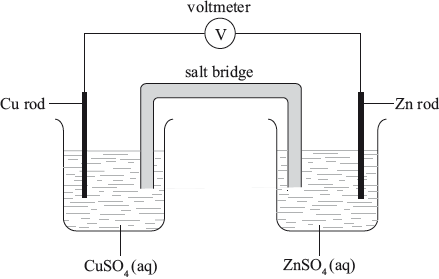

A voltaic cell is made by connecting a copper half-cell, \({\text{Cu(s)}}\left| {{\text{C}}{{\text{u}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}}} \right.\), to an iron half-cell \({\text{Fe(s)}}\left| {{\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}}} \right.\).

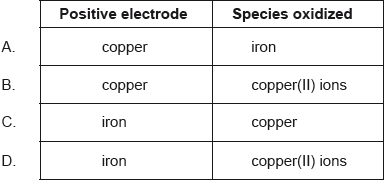
Which combination correctly identifies the positive electrode and the species being oxidized?
Which species is oxidized in the following reaction?
\[{\text{2A}}{{\text{g}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{Cu(s)}} \to {\text{2Ag(s)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{u}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}}\]
A. \({\text{A}}{{\text{g}}^ + }\)
B. Cu
C. Ag
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{u}}^{2 + }}\)
Which equation shows oxygen undergoing reduction?
A. 2F2 + O2 → 2F2O
B. Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH
C. H2O2 + 2HI → 2H2O + I2
D. 2CrO42− + 2H+ \( \rightleftharpoons \) Cr2O72− + H2O
Which coefficients correctly balance this redox equation?
aFe2+(aq) + MnO4−(aq) + bH+(aq) → cFe3+(aq) + Mn2+(aq) + dH2O(l)

Which process occurs during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride?
A. Oxidation occurs at the positive electrode (anode).
B. Electrons move through the electrolyte.
C. Sodium ions move through the electrolyte to the positive electrode (anode).
D. Chloride ions move through the electrolyte and are reduced at the negative electrode (cathode).
Which process occurs when a molten salt is electrolysed?
A. The metal ion is oxidized and deposited on the negative electrode (cathode).
B. The metal ion is reduced and deposited on the negative electrode (cathode).
C. The metal ion is oxidized and deposited on the positive electrode (anode).
D. The metal ion is reduced and deposited on the positive electrode (anode).
Which statement is correct for the electrolysis of molten lead iodide, \({\text{Pb}}{{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}\)?
A. Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
B. \({\text{P}}{{\text{b}}^{2 + }}\) ions are oxidized at the negative electrode (cathode).
C. \({{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}\) is produced at the positive electrode (anode).
D. Ions are produced at both electrodes.
Consider the following reaction.
\[{\text{MnO}}_4^ - ({\text{aq)}} + 8{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} + 5{\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}} \to {\text{M}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}} + 5{\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }}{\text{(aq)}} + 4{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(l)}}\]
Which statement is correct?
A. \({\text{MnO}}_{\text{4}}^ - \) is the oxidizing agent and it loses electrons.
B. \({\text{MnO}}_{\text{4}}^ - \) is the reducing agent and it loses electrons.
C. \({\text{MnO}}_{\text{4}}^ - \) is the oxidizing agent and it gains electrons.
D. \({\text{MnO}}_{\text{4}}^ - \) is the reducing agent and it gains electrons.
Which is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction?
\[{\text{5S}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{2IO}}_3^ - {\text{(aq)}} + {\text{4}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} \to {\text{5SO}}_4^{2 - }{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{I}}_2}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{8}}{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}}\]
A. \({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\)
B. \({\text{IO}}_{\text{3}}^ - \)
C. \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\)
D. \({\text{SO}}_{\text{4}}^{2 - }\)
What are the products of the electrolysis of molten zinc bromide?

Which represents a redox reaction?
A. \({\text{NaH(s)}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(l)}} \to {\text{NaOH(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}}\)
B. \({\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(s)}} \to {\text{CaO(s)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}}\)
C. \({\text{CuC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S(aq)}} \to {\text{CuS(s)}} + {\text{2KCl(aq)}}\)
D. \({\text{HCl(aq)}} + {\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(aq)}} \to {\text{NH}}_{\text{4}}^ + {\text{C}}{{\text{L}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}}\)
Which list represents the halogens in increasing order of oxidizing strength (weakest oxidizing agent first)?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\quad {{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}\quad {\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}\)
B. \({{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}\quad {\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}\quad {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\)
C. \({{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}\quad {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\quad {\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\quad {\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}\quad {{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}\)
Which statement about the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride is correct?
A. A yellow-green gas would be produced at the negative electrode.
B. A silvery metal is produced at the positive electrode.
C. Chloride ions are attracted to the positive electrode and undergo oxidation.
D. Sodium ions are attracted to the negative electrode and undergo oxidation.
What happens to iodine when iodate ions, \({\text{IO}}_3^ - \), are converted to iodine molecules, \({{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}\)?
A. It undergoes reduction and its oxidation number changes from \( - 1\) to 0
B. It undergoes oxidation and its oxidation number changes from \( - 1\) to 0
C. It undergoes reduction and its oxidation number changes from \( + 5\) to 0
D. It undergoes oxidation and its oxidation number changes from \( + 5\) to 0
In which species does sulfur have an oxidation number of 0?
A. \({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({{\text{S}}_{\text{8}}}\)
C. \({\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\)
D. \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}\)
Which species can oxidize ethanol to ethanoic acid?
A. \({{\text{I}}^ - }\)
B. Fe
C. \({{\text{O}}^{2 - }}\)
D. Acidified \({{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}\)
What are the correct oxidation numbers of chromium in \({\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}^{{\text{2}} - }\) and manganese in \({\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\)?

Two half-cells are connected via a salt bridge to make a voltaic cell. Which statement about this cell is correct?
A. Oxidation occurs at the positive electrode (cathode).
B. It is also known as an electrolytic cell.
C. Ions flow through the salt bridge.
D. It requires a power supply to operate.
What are the correct names for \({\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\) and \({{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}\), using oxidation numbers?
A. Potassium permanganate and potassium dichromate
B. Potassium manganate(IV) and potassium chromate(VII)
C. Potassium permanganate(IV) and potassium dichromate(VII)
D. Potassium manganate(VII) and potassium dichromate(VI)
What are the oxidation states of each element in \({{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cr}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\)?

Consider the overall reaction taking place in a voltaic cell.
\[{\text{A}}{{\text{g}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(s)}} + {\text{Zn(s)}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(l)}} \to {\text{2Ag(s)}} + {\text{Zn(OH}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(s)}}\]
What is the role of zinc in the cell?
A. The positive electrode and the oxidizing agent.
B. The positive electrode and the reducing agent.
C. The negative electrode and the oxidizing agent.
D. The negative electrode and the reducing agent.
At which electrodes does oxidation occur in a voltaic cell and in an electrolytic cell?

Which statement is correct about a reducing agent?
A. It is reduced by gaining electrons.
B. It is oxidized by gaining electrons.
C. It is oxidized by losing electrons.
D. It is reduced by losing electrons.
What is the coefficient for I– when the following equation is balanced using the smallest possible whole numbers?
\({\text{IO}}_{_3}^ - {\text{(aq)}} + \) ___ \({{\text{I}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}} + \) ___ \({{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} \to \) ___ \({{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(aq)}} + \) ___ \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(l)}}\)
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 5
What is the name of \({\text{C}}{{\text{o}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{(P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\)?
A. Cobalt(II) phosphite
B. Cobalt(II) phosphate
C. Cobalt(III) phosphite
D. Cobalt(III) phosphate
Consider the following reaction.
\[{\text{Sn(s)}} + {\text{4HN}}{{\text{O}}_3}{\text{(aq)}} \to {\text{Sn}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(s)}} + {\text{4N}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(g)}}\]
Which statement is correct?
A. \({\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\) is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes oxidation.
B. \({\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\) is the reducing agent because the oxidation number of nitrogen changes from \( + 5\) to \( + 4\).
C. Sn is the oxidizing agent because it undergoes reduction.
D. Sn is the reducing agent because the oxidation number of tin changes from 0 to \( + 4\).
Which species of vanadium has a different oxidation number from the rest?
A. \({\text{VO}}_2^ + \)
B. \({\text{VO}}_3^ - \)
C. \({{\text{V}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{5}}}\)
D. \({\text{V}}{{\text{O}}^{2 + }}\)
What is the correct systematic name of MnO2?
A. Manganese(II) oxide
B. Manganese(IV) oxide
C. Magnesium(II) oxide
D. Magnesium(IV) oxide
Which statement about an electrolytic cell is correct?
A. Chemical energy is converted to electrical energy.
B. Electrons move through the electrolyte.
C. The cathode is the negative electrode.
D. The negative ions move towards the negative electrode.
A voltaic cell is constructed from zinc and copper half-cells. Zinc is more reactive than copper. Which statement is correct when this cell produces electricity?
A. Electrons flow from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell.
B. The concentration of Cu2+ (aq) increases.
C. Electrons flow through the salt bridge.
D. Negative ions flow through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the zinc half-cell.
A voltaic cell is made by connecting zinc and lead half-cells. The overall equation for the reaction occurring in the cell is shown below.
\[{\text{Zn(s)}} + {\text{P}}{{\text{b}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}} \to {\text{Pb(s)}} + {\text{Z}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}}\]
Which statements are correct when the cell produces electricity?
I. The zinc is oxidized.
II. Electrons move from zinc to lead in the external circuit.
III. The mass of the lead electrode increases.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which statements are correct for the electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide, \({\text{PbB}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(l)}}\)?
I. \({\text{P}}{{\text{b}}^{2 + }}\) is reduced at the negative electrode (cathode).
II. \({\text{B}}{{\text{r}}^ - }\) is oxidized at the positive electrode (anode).
III. Bubbles of a brown gas are observed at the negative electrode (cathode).
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
What are the oxidation states of chromium in (NH4)2Cr2O7 (s) and Cr2O3 (s)?
Which of the following does not react with dilute HCl(aq)?
A. Na2CO3
B. Cu
C. Zn
D. CuO
What is the reaction type and major product at the anode (positive electrode) when molten sodium chloride is electrolysed using platinum electrodes?